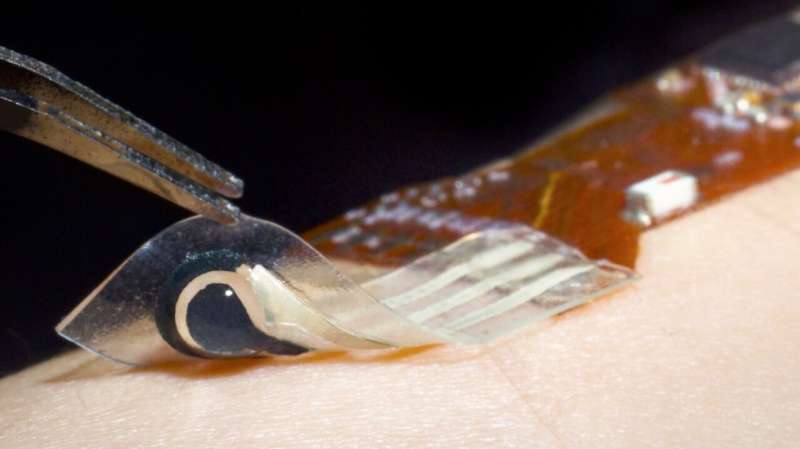
The sensor includes an ionic digital bilayer hydrogel that may detect strong state biomarkers from the pores and skin. The sensor is linked to a versatile printed circuit board which transmits knowledge wirelessly to a person interface. Credit score: NUS iHealthtech
Detecting illnesses early requires the speedy, steady and handy monitoring of important biomarkers. Researchers from the Nationwide College of Singapore (NUS) and the Company for Science, Know-how and Analysis (A*STAR) have developed a novel sensor that permits the continual and real-time detection of solid-state epidermal biomarkers (SEB), a brand new class of well being indicators.
Collectively led by Assistant Professor Liu Yuxin from the NUS Institute for Well being Innovation & Know-how in addition to N.1 Institute for Well being and the Division of Biomedical Engineering underneath the NUS Faculty of Design and Engineering, and Dr. Yang Le, Principal Scientist and Head of the Sensors and Versatile Electronics Division of A*STAR’s Institute of Supplies Analysis and Engineering (A*STAR’s IMRE), the analysis group’s innovation gives a noninvasive technique to watch well being by detecting biomarkers resembling ldl cholesterol and lactate—straight on the pores and skin.
The group’s wearable, stretchable, hydrogel-based sensor overcomes the constraints of present strategies that depend on biofluid samples, resembling blood, urine and sweat. This makes it a promising different for wearable, steady, and real-time well being monitoring, facilitating the early detection of circumstances resembling cardiovascular illnesses and stroke.
It will possibly additionally effectively monitor athletes’ lactate ranges, a sign of exhaustion and tissue hypoxia, which have an effect on their efficiency. This improvement is particularly pertinent to areas together with continual illness administration, population-wide screening, distant affected person monitoring and sport physiology.
The group’s findings have been revealed within the journal Nature Supplies on 12 June 2024. A*STAR’s Institute of Excessive Efficiency Computing and Institute of Molecular and Cell Biology, in addition to Nanyang Technological College, Singapore additionally contributed to the analysis.
Innovating to beat current challenges
Monitoring biomarkers—chemical compounds present in blood or different physique fluids that seize what is occurring in a cell or an organism at a given second—historically entails analyzing biofluids resembling blood, urine and sweat. Whereas efficient, these strategies include challenges.
Blood assessments are invasive and inconvenient, whereas urine analyses could be cumbersome and lack real-time functionality. Probing biomarkers from sweat, although noninvasive, is proscribed by the issue of inducing sweat in inactive people and the discomfort of utilizing sweat-inducing medication. All these pose obstacles to the early prognosis and therapy of illnesses.
SEBs supply a compelling different. These biomarkers, which embrace ldl cholesterol and lactate, are discovered within the stratum corneum, the outermost layer of the pores and skin, and have proven sturdy correlations with illnesses resembling heart problems and diabetes. Nevertheless, detecting these biomarkers straight has been tough. For example, conventional strong electrodes lack the mandatory cost transport pathways to allow electrochemical sensing of SEBs.
The NUS and A*STAR analysis group has overcome this problem with their novel sensor design. When the machine is worn on the pores and skin, SEBs dissolve into the ionic conductive hydrogel (ICH) layer, diffuse by way of the hydrogel matrix, and endure electrochemical reactions catalyzed by enzymes on the junction between the ICH and electronically conductive hydrogel (ECH) layer.
Related physiological knowledge is then transmitted wirelessly to an exterior person interface through a versatile printed circuit board, offering steady monitoring capabilities. The sensor is produced utilizing a scalable and cost-effective manufacturing course of referred to as display printing.
“Our novel hydrogel sensor know-how is essential to enabling the noninvasive detection of solid-state biomarkers on pores and skin. The ionic conductive hydrogel layer that solvates the biomarkers and the electronically conductive hydrogel layer facilitates electron transport.
“This bilayer allows the sequential solvation, diffusion and electrochemical response of the biomarkers. One other spotlight is the sensor’s sensitivity with biomarkers being detected exactly even in low quantities,” stated Asst. Prof. Liu.
“This wearable sensor is the first-in-the-world that may monitor biomarkers on dry or non-sweaty pores and skin. The sensor’s novel bilayer hydrogel electrode interacts with and detects biomarkers on our pores and skin, permitting them to develop into a brand new class of well being indicators. The stretchable design enhances consolation and accuracy as nicely, by adapting to our pores and skin’s pure elasticity.
“This innovation can change the best way we strategy well being and way of life monitoring, notably for these dwelling with continual circumstances requiring fixed well being monitoring,” stated Dr. Yang.
Dependable, delicate and user-friendly
Not like conventional sensors that require biofluid samples, this sensor can repeatedly and noninvasively monitor SEBs straight on the pores and skin, making it invaluable for distant affected person monitoring and population-wide well being screening.
In medical research, the sensor demonstrated sturdy correlations between the biomarkers detected on the pores and skin and people present in blood samples. This validates the sensor’s accuracy and reliability, suggesting it may very well be an alternative choice to blood assessments for monitoring continual illnesses resembling diabetes, hyperlipoproteinemia and cardiovascular circumstances.
The sensor’s sensitivity is one other benefit, as it will possibly detect solid-state lactate and ldl cholesterol at very low ranges. This degree of sensitivity approaches that of mass spectrometry, which ensures exact monitoring of those biomarkers.
Moreover, the sensor’s design reduces movement artifacts, which happen when the person’s actions have an effect on the position of the sensor or its contact stress to the pores and skin, by thrice in comparison with standard counterparts. This new discovering was efficiently modeled mathematically. By minimizing disruptions brought on by motion, the bilayer hydrogel ensures constant and dependable readings, whereas the stretchable, skin-like nature of the machine enhances person consolation.
“One of many potential functions of this know-how is to interchange the being pregnant diabetic take a look at, generally referred to as the glucose tolerance take a look at. Slightly than topic pregnant ladies to a number of blood attracts, our sensor may very well be used to trace real-time sugar ranges conveniently in a sufferers’ dwelling, with an identical degree of accuracy as conventional assessments. This additionally could be utilized to diabetes generally, changing the necessity for normal finger-prick assessments,” Asst. Prof. Liu defined.
“One other potential utility is to make use of the sensor within the day by day monitoring of coronary heart well being, as heart problems accounts for nearly one-third of deaths in Singapore. The analysis group has launched into a analysis program to work carefully with cardiologists in establishing medical correlation between biomarkers—lactate, ldl cholesterol, and glucose—with coronary heart well being,” stated Dr. Yang.
Rolling out next-gen sensors
The NUS and A*STAR researchers plan to boost the sensor’s efficiency by rising its working time and sensitivity. Additional, they intention to combine further solid-state analytes, broadening the sensor’s applicability to different biomarkers.
The researchers are additionally collaborating with hospitals to supply further medical validation and convey the know-how to sufferers, notably for steady glucose monitoring, in addition to quantitative evaluation of dynamic resilience.
Extra data:
Ruth Theresia Arwani et al, Stretchable ionic–digital bilayer hydrogel electronics allow in situ detection of solid-state epidermal biomarkers, Nature Supplies (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41563-024-01918-9
Offered by
Nationwide College of Singapore
Quotation:
Wearable, stretchable sensor allows fast, steady, noninvasive detection of solid-state pores and skin biomarkers (2024, August 19)
retrieved 19 August 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/information/2024-08-wearable-stretchable-sensor-enables-quick.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.

















