The rise within the U.S. calorie provide accountable for the weight problems epidemic wasn’t nearly extra meals, however a distinct type of meals.
The rise within the variety of energy supplied by the meals provide for the reason that Nineteen Seventies “is greater than ample to elucidate the US epidemic of weight problems.” Related spikes in calorie surplus had been famous in developed nations all over the world in parallel with and presumed to be primarily accountable for, the increasing waistlines of their populations. After taking exports into consideration, by the yr 2000, the US was producing 3,900 energy for each man, lady, and little one—almost twice as a lot as many individuals want.
It wasn’t at all times this fashion. The variety of energy within the meals provide really declined over the primary half of the 20 th century and solely began its upward climb to unprecedented heights within the Nineteen Seventies. The drop within the first half of the century was attributed to the discount in onerous guide labor. The inhabitants had decreased vitality wants, in order that they ate decreased vitality diets. They didn’t want all the additional energy. However then the “vitality stability flipping level” occurred, when the “transfer much less, keep lean section” that existed all through many of the century became the “eat extra, acquire weight section” that plagues us to this present day. So, what modified?
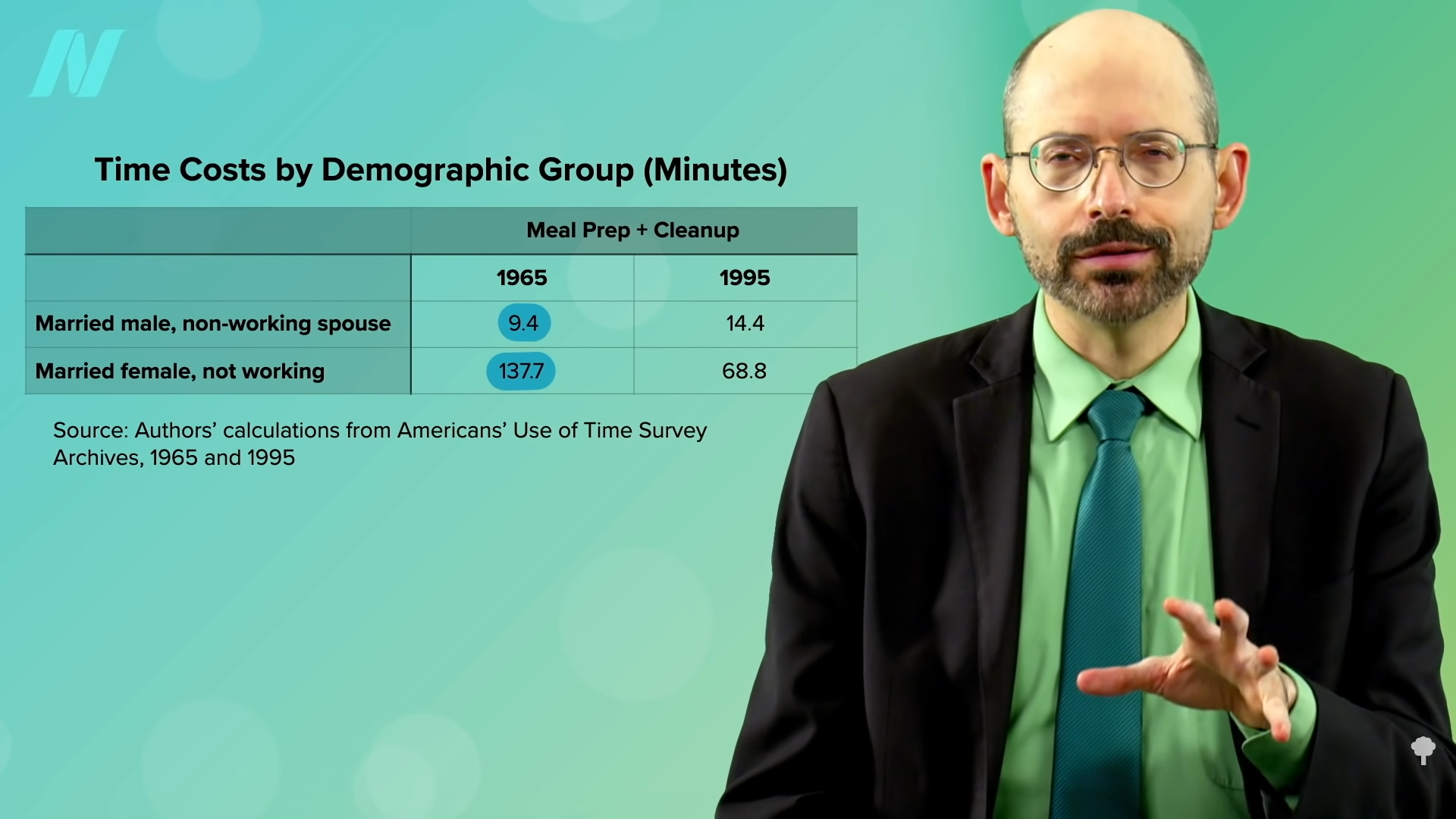
As I talk about in my video The Position of Processed Meals within the Weight problems Epidemic, what occurred within the Nineteen Seventies was a revolution within the meals trade. Within the Sixties, most meals was ready and cooked within the house. The standard “married feminine, not working” spent hours a day cooking and cleansing up after meals. (The “married male, non-working partner” averaged 9 minutes, as you may see under and at 1:34 in my video.) However then a mixed-blessing transformation happened. Technological advances in meals preservation and packaging enabled producers to mass put together and distribute meals for prepared consumption. The metamorphosis has been in comparison with what occurred a century earlier than with the mass manufacturing and provide of manufactured items throughout the Industrial Revolution. However this time, they had been simply mass-producing meals. Utilizing new preservatives, synthetic flavors, and methods, akin to deep freezing and vacuum packaging, meals firms might make the most of economies of scale to mass produce “very sturdy, palatable, and ready-to-consume” edibles that supply “an unlimited business benefit over contemporary and perishable entire or minimally processed meals.”
Suppose ye of the Twinkie. With sufficient effort and time, “bold cooks” might create a cream-filled cake, however now they’re out there round each nook for lower than a greenback. If each time somebody needed a Twinkie, they needed to bake it themselves, they’d in all probability eat rather a lot fewer Twinkies. The packaged meals sector is now a multitrillion-dollar trade.
Think about the standard potato. We’ve lengthy been a nation of potato eaters, however we often baked or boiled them. Anybody who’s made fries from scratch is aware of what a ache it’s, with all of the peeling, chopping, and splattering of oil. However with refined machinations of mechanization, manufacturing turned centralized and fries might be shipped at -40°F to any fast-food deep-fat fryer or frozen meals part within the nation to change into “America’s favourite vegetable.” Practically all the rise in potato consumption in current many years has been within the type of french fries and potato chips.
Cigarette manufacturing affords a compelling parallel. Up till automated rolling machines had been invented, cigarettes needed to be rolled by hand. It took 50 employees to provide the identical variety of cigarettes a machine might make in a minute. The value plunged and manufacturing leapt into the billions. Cigarette smoking went from being “comparatively unusual” to being virtually in every single place. Within the twentieth century, the common per capita cigarette consumption rose from 54 cigarettes a yr to 4,345 cigarettes “simply earlier than the primary landmark Surgeon Basic’s Report” in 1964. The typical American went from smoking about one cigarette every week to half a pack a day.
Tobacco itself was simply as addictive earlier than and after mass advertising. What modified was low-cost, quick access. French fries have at all times been tasty, however they went from being uncommon, even in eating places, to being accessible round every nook (seemingly subsequent to the fuel station the place you will get your Twinkies and cigarettes).
The primary Twinkie dates again to 1930, although, and Ore-Ida began promoting frozen french fries within the Fifties. There needs to be extra to the story than simply technological innovation, and we’ll discover that subsequent.
This explosion of processed junk was aided and abetted by Large Authorities on the behest of Large Meals, which I discover in my video The Position of Taxpayer Subsidies within the Weight problems Epidemic.
That is the fifth video in an 11-part sequence. Listed here are the primary 4:
Movies nonetheless to return are listed within the associated movies under.

















